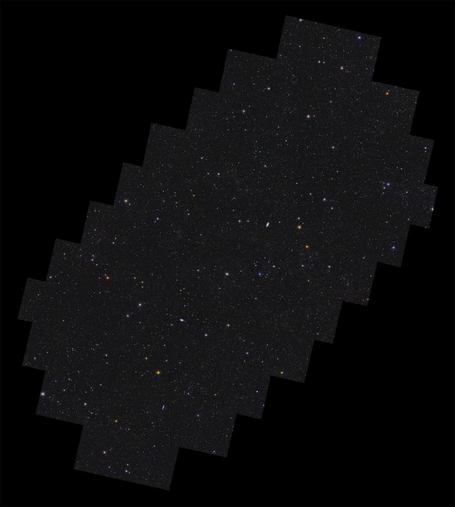
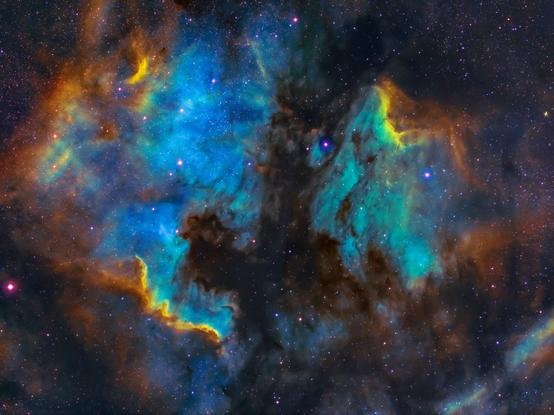
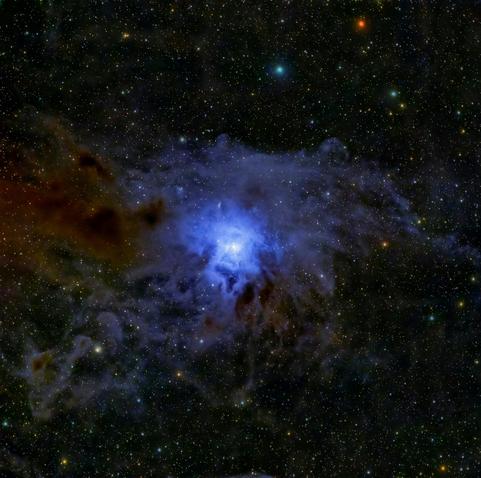
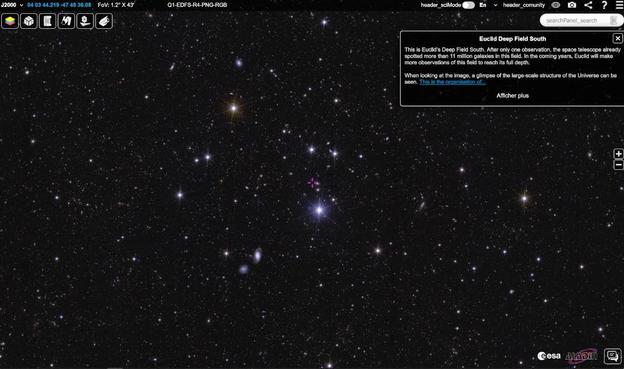
[Zoom on the #CosmicWeb] Have you dived into the deep fields of #Euclid revealed this Wednesday by the @ec_euclid ? Have you navigated between the thousands of #galaxies of different shapes, sizes, colors and masses? So many objects, near and far, fill our #Universe! https://sky.esa.int/esasky/?hide_welcome=true&hide_banner_info=true&hips=DES-DR2+ColorIRG&sci=false&layout=esasky&euclid_image=EDFS
What if their spatial distribution could tell us something about two mysterious components : #DarkMatter and #DarkEnergy? This is the gamble taken by the scientists involved in the Euclid mission. To do so, they've designed some unrivalled #instruments: a camera with great depth of field and high resolution records the variety of shapes and spatial distribution of galaxies, while a #spectrometer coupled with a #photometer can determine the distances and masses of galaxies ...
Alain Blanchard, professor at the University of Toulouse and researcher at IRAP, comments on the consortium's first-ever publication of scientific data: https://www.irap.omp.eu/en/2025/03/euclid-telescope-reports-first-results/