Password auth in Rust, from scratch - Attacks and best practices
https://lpalmieri.com/posts/password-authentication-in-rust/

Password auth in Rust, from scratch - Attacks and best practices
https://lpalmieri.com/posts/password-authentication-in-rust/

Как упростить контроль доступа в приложениях на FastAPI с помощью фреймворка Oso
В разработке современных веб-приложений контроль доступа является одним из критически важных компонентов. Хотя FastAPI предоставляет базовые инструменты для реализации аутентификации и авторизации, они могут оказаться недостаточными для сложных сценариев. Фреймворк Oso предлагает элегантное решение этой проблемы, значительно упрощая процесс и повышая безопасность вашего приложения. Давайте посмотрим, как это можно реализовать.

Released: #swad v0.1
Looking for a simple way to add #authentication to your #nginx reverse proxy? Then swad *could* be for you!
swad is the "Simple Web Authentication Daemon", written in pure #C (+ #POSIX) with almost no external dependencies. #TLS support requires #OpenSSL (or #LibreSSL). It's designed to work with nginx' "auth_request" module and offers authentication using a #cookie and a login form.
Well, this is a first release and you can tell by the version number it isn't "complete" yet. Most notably, only one single credentials checker is implemented: #PAM. But as pam already allows pretty flexible configuration, I already consider this pretty useful
If you want to know more, read here:
https://github.com/Zirias/swad
My son is 12-year old son is creating an online game and asked "why do users have to login to be on the game's leaderboard." This prompted a discussion about how authentication and authorization are often confused and how they play distinct yet complementary roles in protecting each players games scores for his website. I explained the two as follows:
Authentication (AuthN) asks the question "Are you who you say you are?" It verifies an identity using credentials like passwords, biometrics, or MFA.
Authorization (AuthZ) asks "What are you allowed to do?" It determines what actions, or resources, you have access to after authentication.
You authenticate first (prove your identity), then get authorized (granted permissions). Without both, security is incomplete. The two concepts work in concert to prevent unauthorized system access or data tampering.
I know that probably wasn't the coolest conversation between a father and son, but his gaming site now has a user login page. :)
BIO-key Partners with Arrow ECS Iberia to Strengthen Access https://www.byteseu.com/880541/ #AccessManagement #authentication #BIOKeyInternational #biometrics #CloudComputing #GDPR #Iberia #Inc. #Multifactor #Nasdaq:BKYI #NIS2 #Passwordless #Portugal #SingleSignOn #Spain
Trying to come up with my own little self-hosted #http #authentication #daemon to work with #nginx' "authentication request" facility ... first step done!
Now I have a subset of HTTP 1.x implemented in #C, together with a dummy handler showing nothing but a static hello-world root document.
I know it's kind of stubborn doing that in C, but hey, #coding it is great fun

Microsoft Unifies Sign-In Systems for Windows, Xbox, and Microsoft 365
#Microsoft #Windows11 #Xbox #Microsoft365 #Passkeys #CyberSecurity #Authentication #BigTech
Мой опыт настройки SSO OpenID Connect в 1С с помощью Authentik
При внедрении единой системы аутентификации в компании я столкнулся с задачей организовать SSO-доступ к 1С через протокол OpenID Connect. За основу я взял статью на InfoStart ( https://infostart.ru/1c/articles/1538390/ ), однако в качестве провайдера аутентификации использовал не Keycloak, как в оригинале, а Authentik — современную и удобную альтернативу с простым UI и богатым функционалом.

"Franse overheid voert phishingtest uit op 2,5 miljoen leerlingen"
https://www.security.nl/posting/881630/Franse+overheid+voert+phishingtest+uit+op+2%2C5+miljoen+leerlingen
KRANKZINNIG!
Het is meestal onmogelijk om nepberichten (e-mail, SMS, ChatApp, social media en papieren post - zie plaatje) betrouwbaar van echte te kunnen onderscheiden.
Tegen phishing en vooral nepwebsites is echter prima iets te doen, zoals ik vandaag nogmaals beschreef in https://security.nl/posting/881655.
(Big Tech en luie websitebeheerders willen dat niet, dus is en blijft het een enorm gevecht).
Update VMware Tools for Windows Now: High-Severity Flaw Lets Hackers Bypass Authentication – Source: www.techrepublic.com https://ciso2ciso.com/update-vmware-tools-for-windows-now-high-severity-flaw-lets-hackers-bypass-authentication-source-www-techrepublic-com/ #rssfeedpostgeneratorecho #SecurityonTechRepublic #SecurityTechRepublic #CyberSecurityNews #MicrosoftWindows #vulnerabilities #authentication #Cybersecurity #vmwaretools #Networking #Microsoft #broadcom #Security #hackers #VMware #News

Trustly to Pilot Biometric Solution in Finland Before Rollout https://www.byteseu.com/865971/ #authentication #BiometricAuthentication #biometrics #DigitalTransformation #EMEA #Finland #gaming #IdentityVerification #News #PayByBank #PYMNTSNews #Technology #Trustly #TrustlyID #What'sHot
https://www.europesays.com/1944668/ Trustly to Pilot Biometric Solution in Finland Before Rollout #authentication #BiometricAuthentication #Biometrics #DigitalTransformation #EMEA #finland #Gaming #IdentityVerification #News #PayByBank #PYMNTSNews #Suomi #technology #Trustly #TrustlyID #uutiset #What'sHot
@yacc143 FYI: #Passkeys and #FIDO2 (= "device-bound #passkey" which can be divided into "platform-" and "roaming-authenticators") are identical except the #cloud-sync mechanism (as of my current understanding).
So unfortunately, they get mixed up or are considered as totally different things. Both is wrong.
In reality, they are very similar except that FIDO2 hardware tokens ("device-bound passkeys" only in their "roaming-authenticator" variant) are designed that way, that Passkeys are not being able to extracted from the device (at least for the moment).
Therefore, users of HW tokens can't be tricked into transferring their passkey to a rogue third party, which is possible with all other Passkey variants. Therefore: passkeys are NOT #phishing-resistant in the general case.
@mensrea : if you visit a shop (or a bank) in the center of the city, chances are near zero that it's run by impostors.
However, if you go to some vague second hand market, chances are the you will be deceived.
Possibly worse, if there's an ATM on the outside wall of a shack where Hells Angels meet, would you insert your bank card and enter your PIN?
On the web, most people do not know WHERE they are.
Big Tech is DELIBERATELY withholding essential information from people, required to determine the amount of trust that a website deserves.
DELIBERATELY, because big tech can rent much more (cheap) hosting and (meaningless) domain names to whomever if website vistors cannot distinguish between authentic and fake websites.
You are right that some people will never understand why they need to know who owns a website.
However, most people (including @troyhunt ) would enormously benefit.
Like all the other deaf and blind trolls, you trash a proposal because it may be useless for SOME, you provide zero solutions and you keep bashing me.
What part of "get lost" do you not understand?
@mensrea : it is not the UI/UX that is the problem. It is missing reliable info in the certs.
Image from https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/114224682101772569
@aral :
I don't want to pay a cent. Neither donate, nor via taxes.
@aral : most Let's Encrypt (and other Domain Validated) certificates are issued to junk- or plain criminal websites.
They're the ultimate manifestation of evil big tech.
They were introduced to encrypt the "last mile" because Internet Service Providers were replacing ads in webpages and, in the other direction, inserting fake clicks.
DV has destroyed the internet. People loose their ebank savings and companies get ransomwared; phishing is dead simple. EDIW/EUDIW will become an identity fraud disaster (because of AitM phishing atracks).
Even the name "Let's Encrypt" is wrong for a CSP: nobody needs a certificate to encrypt a connection. The primary purpose of a certificate is AUTHENTICATION (of the owner of the private key, in this case the website).
However, for human beings, just a domain name simply does not provide reliable identification information. It renders impersonation a peace of cake.
Decent online authentication is HARD. Get used to it instead of denying it.
REASONS/EXAMPLES
Troy Hunt fell in the DV trap: https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/114222237036021070
Google (and Troy Hunt!) killed non-DV certs (for profit) because of the stripe.com PoC. Now Chrome does not give you any more info than what Google argumented: https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/114224682101772569
https:⧸⧸cancel-google.com/captcha was live yesterday: https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/114224264440704546
Stop phishing proposal: https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/113079966331873386
Lots of reasons why LE sucks:
https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/112914047006977222 (corrected link 09:20 UTC)
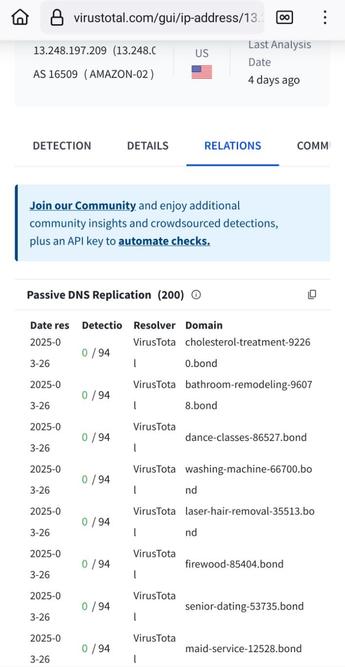
This website stopped registering junk .bond domain names, probably because there were too many every day (the last page I found): https://newly-registered-domains.abtdomain.com/2024-08-15-bond-newly-registered-domains-part-1/. However, this gang is still active, open the RELATIONS tab in https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ip-address/13.248.197.209/relations. You have to multiply the number of LE certs by approx. 5 because they also register subdomains and don't use wildcard certs. Source: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/revolver-rabbit-gang-registers-500-000-domains-for-malware-campaigns/
@BjornW :
I've stopped doing that after a lot of people called me an idiot and a liar if I kindly notified them. I stopped, I'll get scolded anyway.
Big tech and most admins want everyone to believe that "Let's Encrypt" is the only goal. Nearly 100% of tech people believe that.
And admins WANT to believe that, because reliable authentication of website owners is a PITA. They just love ACME and tell their website visitors to GFY.
People like you tooting nonsense get a lot of boosts. It's called fake news or big tech propaganda. If you know better, why don't you WRITE BETTER?
It has ruined the internet. Not for phun but purely for profit. And it is what ruins people's lives and lets employees open the vdoor for ransomware and data-theft.
See also https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/112914047006977222 (and, in Dutch, https://security.nl/posting/881296).
@troyhunt : if we open a website that we've never visited before, we need browsers to show us all available details about that website, and warn us if such details are not available.
We also need better (readable) certificates identifying the responsible / accountable party for a website.
We have been lied to that anonymous DV certificates are a good idea *also* for websites we need to trust. It's a hoax.
Important: certificates never directly warrant the trustworthyness of a website. They're about authenticity, which includes knowing who the owner is and in which country they are located. This helps ensuring that you can sue them (or not, if in e.g. Russia) which *indirectly* makes better identifiable websites more reliable.
More info in https://infosec.exchange/@ErikvanStraten/113079966331873386 (see also https://crt.sh/?Identity=mailchimp-sso.com).
Note: most people do not understand certificates, like @BjornW in https://mastodon.social/@BjornW/114064065891034415:
❝
@letsencrypt offers certificates to encrypt the traffic between a website & your browser.
❞
2x wrong.
A TLS v1.3 connection is encrypted before the website sends their certificate, which is used only for *authentication* of the website (using a digital signature over unguessable secret TLS connection parameters). A cert binds the domain name to a public key, and the website proves possession of the associated private key.
However, for people a domain name simply does not suffice for reliable identification. People need more info in the certificate and it should be shown to them when it changes.
Will you please help me get this topic seriously on the public agenda?
Edited 09:15 UTC to add: tap "Alt" in the images for details.